7.3 KiB
Sub-queries and Views
Agenda
* Sub-queries
* Built-in string functions
Sub-queries
A subquery is a SQL query nested inside a larger query. A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved.
You can use a sub-query in a SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE statement to perform the following tasks:
- Compare an expression to the result of the query.
- Determine if an expression is included in the results of the query.
- Check whether the query selects any rows.
A sub-query may occur in :
- A SELECT clause
- A FROM clause
- A WHERE clause
There are a few rules that sub-queries must follow −
- Sub-queries must be enclosed within parentheses.
- A sub-query can have only one column in the SELECT clause, unless multiple columns are in the main query for the sub-query to compare its selected columns.
- An ORDER BY command cannot be used in a subquery, although the main query can use an ORDER BY.
- Sub-queries that return more than one row can only be used with multiple value operators such as the IN operator.
- The BETWEEN operator cannot be used with a subquery. However, the BETWEEN operator can be used within the subquery.
Let us consider the students table below
| id | first_name | last_name | batch_id | iq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Watson | 1 | 120 |
| 2 | Mycroft | Holmes | 1 | 160 |
| 3 | Moriarty | Patel | 2 | 160 |
Now, we want all the students who are greater than the average IQ.
We can compute the average IQ using the AVG function but the aggregated value can not be used within the WHERE clause. So, let us try to use a sub-query.
SELECT
first_name, last_name, iq
FROM
students
WHERE
iq > (SELECT
AVG(iq)
FROM
students);
This would first compute the average IQ of all the students and then compare the average IQ to the IQ of the current student. Since the sub-query returns a single value, it can be used in the WHERE clause without any special handling.
Let us modify the original query to see an example where the sub-query returns multiple values. We want all the students who have IQs greater than the students of batch_id 2;
One way to handle this query is to use the MAX function to get the highest IQ of the batch_id 2 students.
SELECT
*
FROM
students
WHERE
iq > (SELECT
MAX(iq)
FROM
students
WHERE
batch_id = 2);
Another way would be to use the ALL keyword. ALL means that the condition will be true only if the operation is true for all values in the range.
SELECT
*
FROM
students
WHERE
iq > ALL (SELECT
iq
FROM
students
WHERE
batch_id = 2);
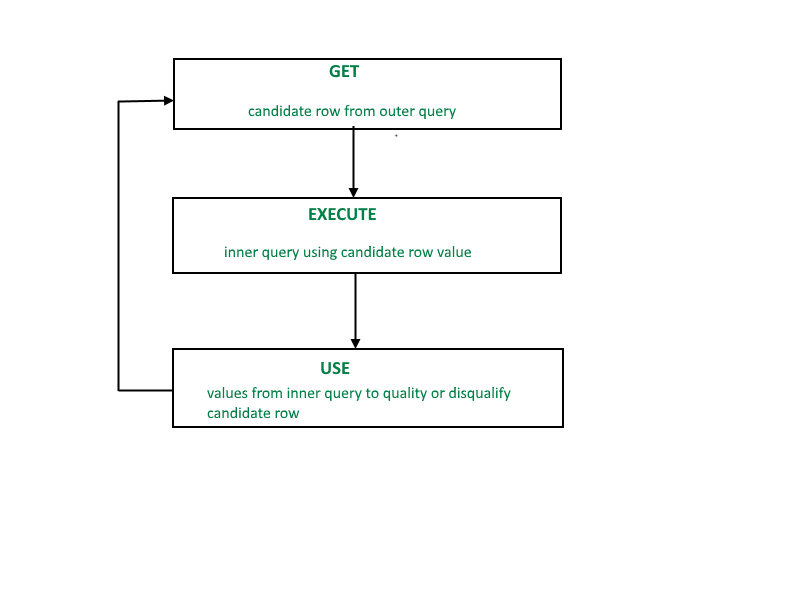
Correlated Sub-queries
A correlated subquery (also known as a synchronized subquery) is a subquery (a query nested inside another query) that uses values from the outer query. Because the subquery may be evaluated once for each row processed by the outer query, it can be slow.
Correlated subqueries are used for row-by-row processing. Each subquery is executed once for every row of the outer query.
A correlated subquery is one way of reading every row in a table and comparing values in each row against related data. It is used whenever a subquery must return a different result or set of results for each candidate row considered by the main query.
In other words, you can use a correlated subquery to answer a multipart question whose answer depends on the value in each row processed by the parent statement.
EXISTS operator
The EXISTS operator tests for existence of rows in the results set of the subquery. If a subquery row value is found the condition is flagged TRUE and the search does not continue in the inner query, and if it is not found then the condition is flagged FALSE and the search continues in the inner query.
MySQL functions
MySQL has a number of built-in functions that can be used to perform common tasks. They are divided in the following categories:
- Numeric
- String
- Date and time
- Miscellaneous
Numeric functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Absolute value | SELECT ABS(-1) |
| CEIL | Round up to the nearest integer | SELECT CEIL(1.5) |
| FLOOR | Round down to the nearest integer | SELECT FLOOR(1.5) |
| ROUND | Round to the given precision | SELECT ROUND(1.54, 1) |
| TRUNCATE | Truncate to the given precision | SELECT TRUNCATE(1.54, 1) |
| RAND | Generate a random number | SELECT RAND() |
See more function here.
String functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| LENGTH | Length of the string | SELECT LENGTH('Kattapa') |
| LOWER | Convert to lowercase | SELECT LOWER('Kattapa') |
| UPPER | Convert to uppercase | SELECT UPPER('Kattapa') |
| LTRIM | Trim leading spaces | SELECT LTRIM(' Kattapa') |
| RTRIM | Trim trailing spaces | SELECT RTRIM('Kattapa ') |
| TRIM | Trim leading and trailing spaces | SELECT TRIM(' Kattapa ') |
| SUBSTR | Extract a substring | SELECT SUBSTR('Namma Bengaluru', 1, 3) |
| LEFT | Extract left substring | SELECT LEFT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
| RIGHT | Extract right substring | SELECT RIGHT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
| LOCATE | Find the position of a substring | SELECT LOCATE('Bengaluru', 'Namma Bengaluru') |
See more function here.
Date and time functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| NOW | Current date and time | SELECT NOW() |
| CURDATE | Current date | SELECT CURDATE() |
| CURTIME | Current time | SELECT CURTIME() |
| YEAR | Year of the date | SELECT YEAR('2020-01-01') |
| MONTH | Month of the date | SELECT MONTH('2020-01-01') |
| DAY | Day of the date | SELECT DAY('2020-01-01') |
| DAYNAME | Day of the week | SELECT DAYNAME('2020-01-01') |
| DAYOFWEEK | Day of the week | SELECT DAYOFWEEK('2020-01-01') |
| DATE_ADD | Add a date | SELECT DATE_ADD('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
| DATE_SUB | Subtract a date | SELECT DATE_SUB('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
| DATEDIFF | Difference between two dates | SELECT DATEDIFF('2020-01-01', '2020-01-02') |
Miscellaneous functions
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| IFNULL | Replace NULL values | SELECT IFNULL(batch_id, 'NO BATCH') |
| COALESCE | Replace NULL values recursively | SELECT COALESCE(batch_id, phone, email, first_name) |
| IF | Conditional expression | SELECT IF(batch_id = 1, 'YES', 'NO') |
| CASE | Conditional expression | SELECT CASE WHEN batch_id = 1 THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END |