5.7 KiB
Java Architecture
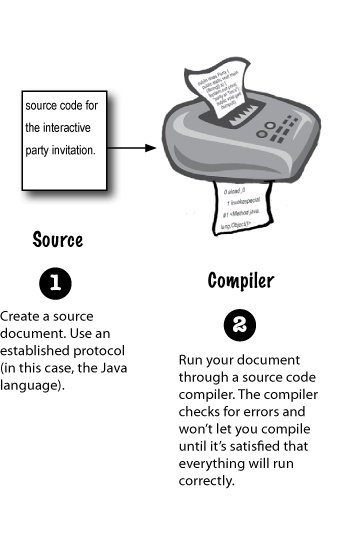
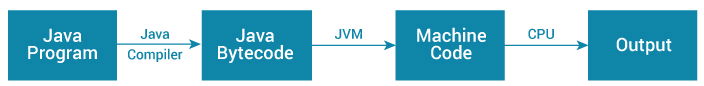
Java is a platform-independent language. For that we need to understand the steps of compilation and execution of code.
- The code written in Java, is converted into byte codes which is done by the Java Compiler
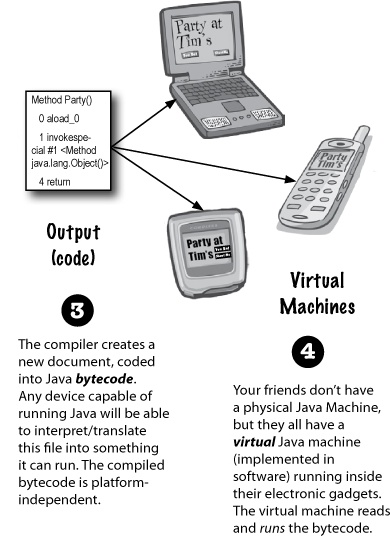
- The byte code, is converted into machine code by the JVM.
- The Machine code is executed directly by the machine.
Bytecodes are effectively platform-independent. The java virtual machine takes care of the differences between the bytecodes for the different platforms. This makes the Java Compiled Code platform independent.
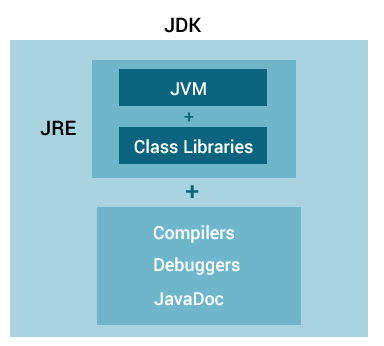
There are three main components of Java architechure: JVM, JRE, and JDK. Java Virtual Machine, Java Runtime Environment and Java Development Kit respectively. Lets understand them one by one.
JVM
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine(software) that enables your computer to run a Java program.
When you run the Java program, Java compiler -javac first compiles your Java code to bytecode. Then, the JVM translates bytecode into native machine code (set of instructions that a computer's CPU executes directly). JVM comes with JIT(Just-in-Time) compiler that converts Java source code into low-level machine language. Hence, it runs more faster as a regular application.
JRE
JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is a software package that provides Java class libraries, Java Virtual Machine (JVM), and other components that are required to run Java applications. JRE is the superset of JVM.
When our software tends to execute a particular program, it requires some environment to run in. Usually, it’s any operating system for example, Unix, Linux, Microsoft Windows, or the MacOS. Here our JRE acts as a translater and also a facilitator between the java program and the operating system.
JDK
JDK (Java Development Kit) is a software development kit required to develop applications in Java. When you download JDK, JRE is also downloaded with it.
In addition to JRE, JDK also contains a number of development tools (compilers, JavaDocs, Java Debugger, etc).
JVM Deep Dive
Java applications are platform independent - write once, run anywhere. This is because of JVM which performs the following tasks -
- Loads the code
- Verifies the code
- Executes the code
- Provides runtime environment
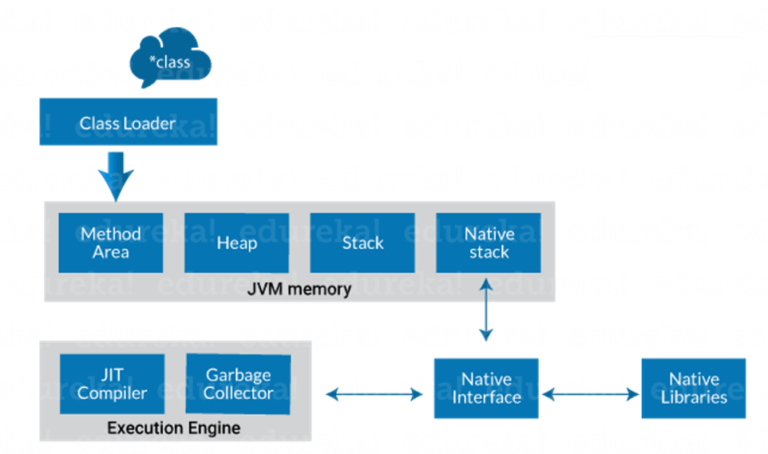
Here are the important components of JVM architecture:
1. Class Loader The class loader is a subsystem used for loading class files. It performs three major functions viz. Loading, Linking, and Initialization.Whenever we run the java program, class loader loads it first.
2. Method Area It is one of the Data Area in JVM, in which Class data will be stored. Static Variables, Static Blocks, Static Methods, Instance Methods are stored in this area. JVM Method Area stores structure of class like metadata, the code for Java methods, and the constant runtime pool.
3. Heap A heap is created when the JVM starts up. It may increase or decrease in size while the application runs. All the Objects, arrays, and instance variables are stored in a heap. This memory is shared across multiple threads.
4. JVM language Stacks Java language Stacks store local variables, and its partial results. Each and every thread has its own JVM language stack, created concurrently as the thread is created. A new stack frame is created when method is invoked, and it is removed when method invocation process is complete. JVM stack is known as a thread stack.
5. PC Registers PC registers store the address of the Java virtual machine instruction, which is currently executing. In Java, each thread has its separate PC register.
6. Native Method Stacks
Native method stacks hold the instruction of native code depends on the native library. It allocates memory on native heaps or uses any type of stack.
7) Execution Engine Execution Engine is the brain of JVM. It has two components.
- JIT compiler
- Garbage collector
JIT compiler: The Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler is a part of the runtime environment. It helps in improving the performance of Java applications by compiling bytecodes to machine code at run time. The JIT compiler is enabled by default. When a method is compiled, the JVM calls the compiled code of that method directly. The JIT compiler compiles the bytecode of that method into machine code, compiling it “just in time” to run.
Garbage collector: As the name explains that Garbage Collector means to collect the unused material. Well, in JVM this work is done by Garbage collection. It tracks each and every object available in the JVM heap space and removes unwanted ones. Garbage collector works in two simple steps known as Mark and Sweep:
Mark – it is where the garbage collector identifies which piece of memory is in use and which are not
Sweep – it removes objects identified during the “mark” phase.
8) Native Method interface
The Native Method Interface is a programming framework. It allows Java code, which is running in a JVM to call by libraries and native applications.
9) Native Method Libraries
Native Libraries is a collection of the Native Libraries (C, C++), which are needed by the Execution Engine.